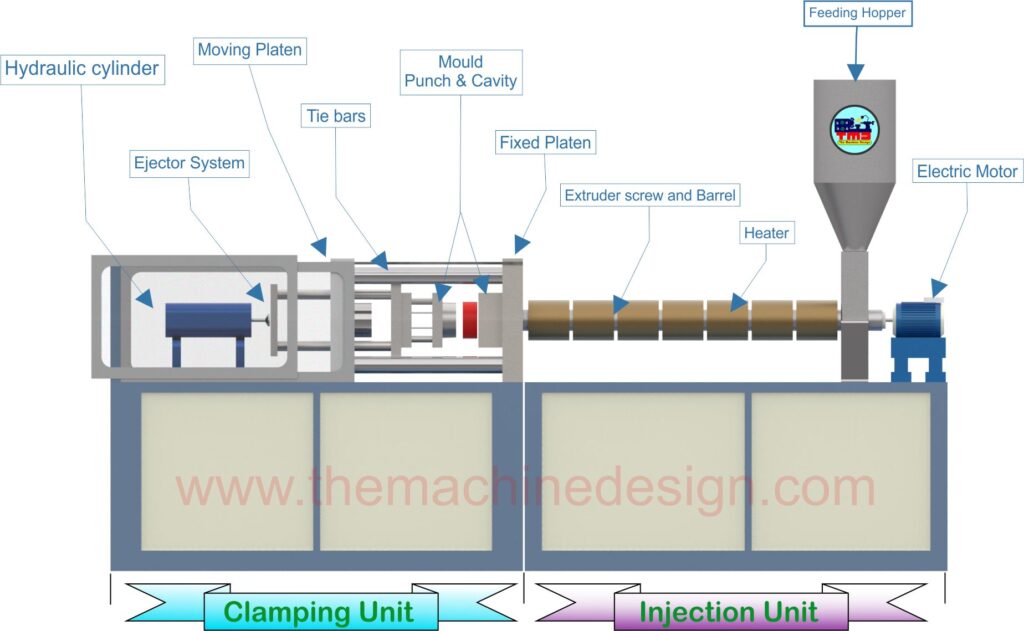
What is Lean Manufacturing? And What are 5 Principles of Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a manufacturing theory, that intends to minimize waste and maximize production efficiency. In the production process, waste is the thing that doesn’t add value for the manufacturer and end-to-end customers. In the lean manufacturing methodology, some specific principles helped improve the production system worldwide. We will discuss these principles in this post as well.

Page Contents
What is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach production system, where Lean practices, tools, resources and principles applied to manufacturing the physical products. At this time, so many manufacturers are using the lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste of efforts, reduce time, cut cost, increase the innovation, process optimization. These principles helps to grow with consistency in the volatile market.
The ultimate object of the the “Lean Manufacturing” is not only to remove waste, – It’s to deliver a real value to the customer.
What are the 5 Principles of Lean Manufacturing?
In The lean manufacturing theory, five core principles defined. These are value, the value stream, flow, pull and perfection. Let’s will discuss in detail.

1. Value –
The first principle of the lean manufacturing is to understand the real value of the ultimate product as per end customer’s perspective. Either customer has willing to pay for the product and service or not. Identification of the product’s feature or services that are the most important to the customer and defining the manufacturing process to to cater those features. After the identifications of the value, manufacturer or service provider has to work on eliminating the wastages from overall process to cut-down the final cost of the product or service.
2. Value Stream –
In the second principle of the lean manufacturing is to create a map of all required process in a stream to deliver the product or service to the customer. The value stream covers the entire lifecycle of a product. This includes all required process in the production, from procuring the raw material to deliver a finished product to the customer and disposal as well.
Each and every process should be inspected for the wastage. Anything that does not added value, that should removed. Mostly, Chain alignment is preferred to achieve lean management.
3. Flow Creation –
After removing waste from the value stream, flow creation ensures to deliver the product or service on time without any delay once ordered. Flow creation is means to removal of functional barriers to improve the lead time. From receiving order to deliver the product, flow creation ensures the process should flow smoothly and constantly.
Some strategies, like balancing the work load, reconfiguration of production steps, and creating additional or cross functional departments can helps to remove the waste from the manufacturing process.
4. Pull System –
The pull system is just opposite of the push system. Push system is used in Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP). In push system inventory need to determined in advance according to the market forecast. However, forecasting isn’t be accurate all the time, this can result in either too much production or short production to meet demand. Due to that additional warehousing costs, handling costs and etc. This can leads to expensiveness and poor customer satisfaction.
In the lean manufacturing, the pull system is used instead of push system. Pull system is depends on the demands. It cannot begin without the previous phase being finished. This is purely relies on communication and flexibility. This system can helps to reduce the warehouse and unnecessary handling cost unlike the push system.
5. Continues Improvement –
The continues improvement in production or service leads to perfection. The continues improvement for perfection is also known as “Kaizen”. The “Kaizen” term is created by Kiichiro Toyoda, the founder of Toyota Motor Corporation. In the lean manufacturing identification and elimination of wastage, improving efficiency and aiming towards excellence is involved.
Also Read:
- 7 Steel Storage Racks for Industrial Workspaces
- Petroleum: Source, Formation and Classification
- What are Hydraulic Turbines?
What are the 8 wastes of Lean Manufacturing?
The 8 wastes of lean manufacturing is termed as “TIMWOODS”. These are as follows:
Transportation – Unnecessary movement of goods and products.
Inventory – Excess Inventory or over stock of raw material or products.
Motion – Unnecessary physical movement of workers or people.
Waiting – Delays or ideal time between processes.
Over-processing – Doing more work than the requirements or adding non-value-added processes.
Overproduction – Producing more than is needed or too early.
Defects – Quality issues or rework.
Skill underutilization – Not utilizing the full capabilities or skills of the workers.
Conclusion:
Lean manufacturing is a methodology that intends to improve the manufacturing process and process flow. This methodology provides benefits to the manufacturer and the end consumer, while saving the time and money by eliminating the wastages.